Mapsy is a Python library designed easily render static maps in python. It is designed to be simple to use and easy to integrate with existing codebases. The library supports rendering background, tiled raster, filled polygon, and other layers on the map. It directly supports geometric primitives, allowing users to directly render shapely geometries.
Input data must be in the EPSG:4326 - WGS84 projection.
| type | status | description | data source |
|---|---|---|---|
BackgroundLayer |
✅ | renders a simple background with a single color | Color |
TiledRasterLayer |
✅ | renders a tiled raster layer can can load xyz tiles | xyz via http(s) |
FillLayer |
✅ | renders a fill layer for polygons | Polygon and MultiPolygon |
LineLayer |
✅ | renders a line layer that draw LineStrings | LineString and MultiLineString |
CircleLayer |
✅ | renders a circle layer for Points | Point and MultiPoint |
SymbolLayer |
✅ | renders a symbol and/or text for points | Point and MultiPoint |
Attribution |
✅ | an attribution | str and list[str] |
You can simply install the library using pip:
pip install mapsyIMPORTANT: This library uses Cairo. You will have to install cairo with your package manager of choice.
on mac
brew install cairoThe Mapsy library is designed to be simple to use. The following sections provide examples of how to create a map with different layers. Note that in almost all cases you would have to add an attribution layer to the map. For example, if you use OpenStreetMap tiles, you would have to add the OpenStreetMap attribution to the map. This is not done automatically!
Here is an example of how to create a simple map with a tiled raster layer:
import mapsy
my_map = mapsy.Map()
tile_layer = mapsy.TiledRasterLayer(
[
"https://tile.openstreetmap.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png",
]
)
my_map.add_layer(tile_layer)
my_map.add_layer(mapsy.Attribution("© OpenStreetMap contributors"))
surf = my_map.render(
mapsy.FixedScreenSize(
mapsy.Box.from_lng_lat(5.988, 47.302, 15.016, 54.983), mapsy.ScreenSize(512, 512)
)
)
surf.write_to_png("my_map.png")A background layer provides a solid color background for the map.
background_layer = mapsy.BackgroundLayer(mapsy.Color(1, 1, 1))
my_map.add_layer(background_layer)A tiled raster layer allows the use of map tiles from sources like OpenStreetMap.
tile_layer = mapsy.TiledRasterLayer(
[
"https://tile.openstreetmap.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png",
]
)
my_map.add_layer(tile_layer)A fill layer can be used to add filled polygons with customizable colors and borders.
from shapely.geometry import shape
polygon = shape(json)
fill_layer = mapsy.FillLayer(
[
mapsy.FillItem(
geometry=polygon,
fill_color=mapsy.Color(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.3),
line_color=mapsy.Color(0, 0, 0),
line_width=2,
)
]
)
my_map.add_layer(fill_layer)A line layer can be used to show LineStrings on the map
from shapely.geometry import shape
line = shape(json)
fill_layer = mapsy.LineLayer(
[
mapsy.LineItem(
geometry=line,
join=mapsy.LineJoin.round,
cap=mapsy.LineCap.round
width=12,
outline_width=3,
outline_color=Colors.BLACK,
)
]
)
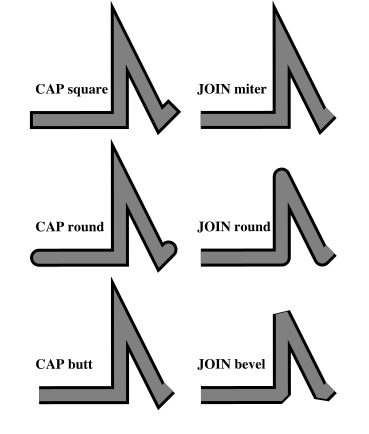
my_map.add_layer(fill_layer)The LineItem options cap and join lead to the following results:
A circle layer can be used to show Points on the map
from shapely.geometry import shape
point = shape(json)
circle_layer = mapsy.CircleLayer(
[
mapsy.CircleItem(
geometry=point,
fill_color=mapsy.Color(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.3),
line_color=mapsy.Color(0, 0, 0),
line_width=2,
radius=10,
)
]
)
my_map.add_layer(circle_layer)A symbol layer can be used to show Points on the map. You can load custom icons by using the mapsy.Icon.from_path class method.
- The text is not automatically placed relative to the symbol. You have to calculate the position yourself.
- No collision detection is implemented. If you place multiple symbols with text on top of each other, the text and symbols will overlap. This might get added in the future, but is somewhat complicated to implement.
from shapely.geometry import shape
point = shape(json)
symbol_layer = mapsy.SymbolLayer(
[
mapsy.SymbolItem(
geometry=point,
icon=mapsy.Icons.PIN_24,
text="Hello World",
text_offset=(0, 16)
)
]
)
my_map.add_layer(symbol_layer)You can set the anchor of the text with the text_anchor parameter. The default is mapsy.TextAnchor.BOTTOM_LEFT. The following options are available:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
An attribution layer can be used to add attribution to the map. This is important if you use tiles from a public source like OpenStreetMap.
attribution = mapsy.Attribution("© OpenStreetMap contributors")
my_map.add_layer(attribution)The project includes unit tests to ensure the functionality of various components. To run the tests, use the following command:
pytestNote that if you have a different cairo version installed some tests might fail. This is due to the fact that the tests compare the rendered images with reference images. If you have a different cairo version installed, the images might look slightly different.
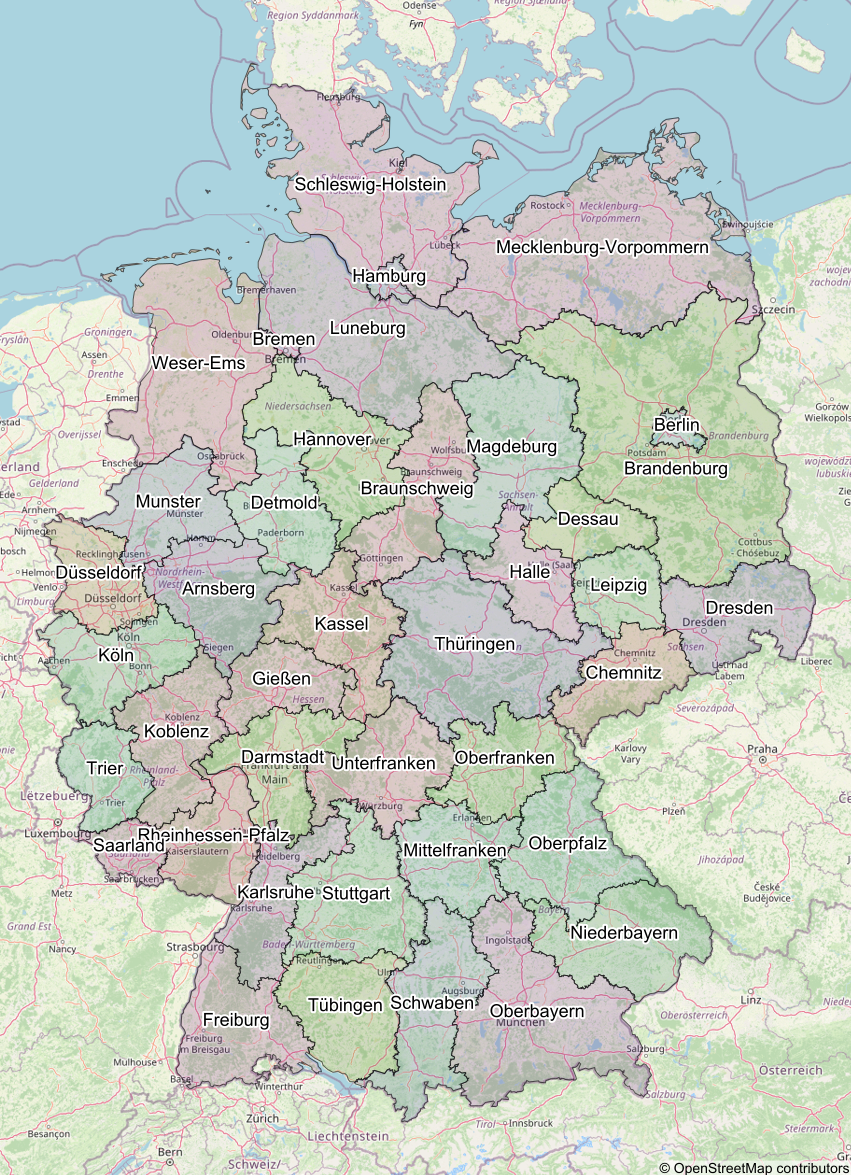
The image below is an example of a map created using the Mapsy library:
This project is licensed under the MIT License.
Contributions are welcome! Please submit a pull request or open an issue for any changes or suggestions.