- General Features
Search term: #IANATimezone
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
With the annotation @Semantics.timeZone you can convert a timezone to one specified according to the IANA standard. You are also able to assign this converted timezone to a timestamp (which has to be in the UTC format) so that the time will be interpreted in this timezone. The annotation to use is @Semantics.timeZoneReference.
The conversion of the timezone is happening at the backend, while the timestamp conversion is done by the UI.
This feature is also available for use with action/function parameters.
In the following example, changing the SAPTimezone field will also change IANATimezone and IANATimestamp, which are both shown in IANA standard and changing Timestamp will change IANATimestamp automatically. This is achieved via side effect.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
// Search Term #IANATimezone
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [{ entity: { name: 'I_TimeZone', element: 'TimeZoneID' } }]
SAPTimezone,
@Semantics.timeZone: true
SAPTimezone as IANATimezone,
Timestamp,
@Semantics.timeZoneReference: 'IANATimezone'
Timestamp as IANATimestamp,
// End Search Term #IANATimezone
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #IANATimezone
@UI.facet: [
{
parentId : 'Nested',
id : 'TimeAndDate',
label : 'Time and Date (#TimeAndDate)',
type : #COLLECTION
},
// Search Term #IANATimezone
{
parentId : 'TimeAndDate',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'TimezoneInput',
label : 'SAP Timezone'
},
{
parentId : 'TimeAndDate',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'TimezoneOutput',
label : 'IANA Timezone'
}
]
@UI.fieldGroup: [
{
qualifier: 'TimezoneInput',
position: 10,
label: 'SAP Timezone'
},
{
qualifier: 'TimezoneInput',
dataAction: 'overwriteTimezone',
type: #FOR_ACTION,
emphasized: true,
label: 'Overwrite Timezone (#IANATimezoneAParameter)'
}
]
SAPTimezone;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{
qualifier: 'TimezoneOutput',
position: 10,
label: 'IANA Timezone (#IANATimezone)'
}]
IANATimezone;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{
qualifier: 'TimezoneInput',
position: 20
}]
Timestamp;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{
qualifier: 'TimezoneOutput',
position: 20,
label: 'IANA Timestamp (#IANATimezone)'
}]
IANATimestamp;
// End Search Term #IANATimezone
Side effects for timezone
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
side effects {
field SAPTimezone affects field IANATimestamp, field IANATimezone;
field Timestamp affects field IANATimestamp;
}
}
Search term: #ValueHelps, #DependentFilter
The implementation of a value help in CDS enables the end user to choose values from a predefined list for input fields on a user interface.
The additional binding defines a second condition for the value help on the same target value help provider entity for filtering the value help result list and/or returning values from the selected value help record. The additional binding can be defined for an additional element or parameter. Depending on the value provided in usage, the additional binding works as a filter, result or filter and result condition
Usage: #Result: The referenced element or parameter in localElement or localParameter is filled with the value provided by the value help. When creating an instance, you can fill various fields with this option.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
// Search Term #ValueHelps
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [
{
entity: { name: '/DMO/FSA_I_Criticality', element: 'Code' },
additionalBinding: [{ element: 'Name',
localElement: 'FieldWithCriticality',
usage: #RESULT }]
}
]
CriticalityCode,
Usage: #Filter : The value of the referenced element or parameter in localElement or localParameter is used as a filter for the value help. The value help only displays filtered results.
// Search Term #DependentFilter
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [
{
entity: { name: '/DMO/FSA_I_Contact', element: 'ID' },
label: 'Contacts',
additionalBinding: [{ element: 'Country',
localElement: 'Country',
usage: #FILTER }]
}
]
ContactID,
You can influence what is shown in the value help using @Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display. In the example below, everything except for ID (Name), phone, country, street, city and postcode would be hidden in the value help.
Note
Source: Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Contact
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Contact
...
{
@ObjectModel.text.element: ['Name'] // Search Term #DisplayTextAndID
@UI.textArrangement: #TEXT_ONLY
@EndUserText.label: 'Contact'
key id as ID,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:false
name as Name,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:true
phone as Phone,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:false
building as Building,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:true
country as Country,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:true
street as Street,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:true
city as City,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:true
postcode as Postcode,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:false
address_label as AddressLabel,
@Consumption.valueHelpDefault.display:false
photo_url as PhotoUrl,
...
}
For smaller collections of possible values in the value help, it might be a good idea to have a dropdown instead of a dialog to choose the value. This can be achieved with the @ObjectModel : { resultSet.sizeCategory: #XS }
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Criticality
@ObjectModel : { resultSet.sizeCategory: #XS }
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Criticality
...
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Providing Value Help
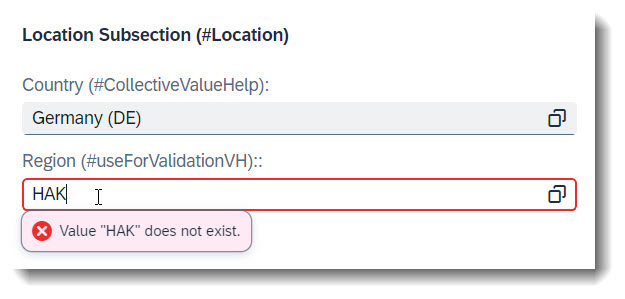
Search term: #useForValidationVH
Warning
Only shown in the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
To mark a value help as an input validator, one can use the keyword useForValidation: true in the annotation @Consumption.valueHelpDefinition. It can be annotated at a field, a CDS parameter or an action parameter.
It is good practice to use the keyword qualifier for every value help, even if the field only has one. If you have defined more than one value help at a field, useForValidation might not work correctly if you have forgotten to use qualifiers, as UI would not be able to determine which value help is to be used for validation.
This keyword does not work for collective value helps.
💡 If you have a draft-enabled app, using this annotation prevents an invalid value from being saved to draft. A refresh of the page will clear the user input.
💡 Another alternative to this annotation would be to use a drop down list with @ObjectModel : { resultSet.sizeCategory: #XS }, if there are not too many available choices.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
// Search Term #useForValidationVH
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [{ entity: { name: 'I_RegionVH', element: 'Region' },
qualifier: 'RegionValueHelp',
useForValidation: true,
additionalBinding: [{ element: 'Country',
localElement: 'Country' }] }]
Region,
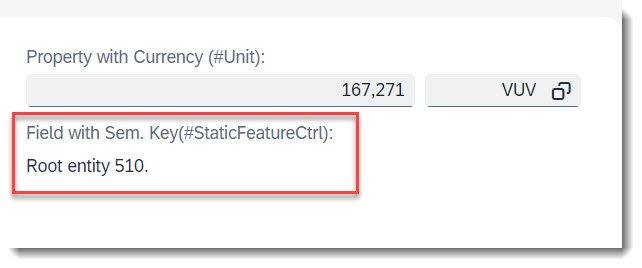
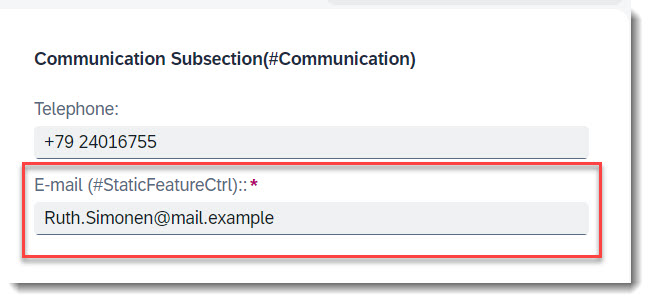
Search term: #StaticFeatureCtrl
Each field can have specific access restrictions, defined in the behaviour definition. If the access restriction is always the same for each instance, you can use static feature control. Some examples/possible combinations are described here:
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
field ( readonly, numbering : managed ) ID;
field ( mandatory ) Email;
field ( mandatory : create, readonly : update ) StringProperty;
}
There are 2 different types of readonly:
field ( readonly, numbering : managed ) ID; means that the field ID is a key that will be assigned a value by the framework (numering:managed) and must not be created or updated by the user at all (readonly). The annotation in $metadata is <Annotation Term="SAP__core.Computed"/>.
field ( mandatory : create, readonly : update ) StringProperty; means that the field StringProperty is only mandatory during create, but after that it will be read only. The annotation for the readonly in $metadata is <Annotation Term="SAP__core.Immutable"/>.
field ( mandatory ) Email; means that the user must provide a value for the field Email. The annotation in $metadata is <Annotation Term="SAP__common.FieldControl" EnumMember="SAP__common.FieldControlType/Mandatory"/>.
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Static Feature Control
Each field can have specific access restrictions, defined in the behaviour definition and behaviour implementation. If the access restriction depends on a certain condition, you can implement the feature control dynamically.
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
field ( features : instance ) TimesChildCreated;
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Implementation /DMO/FSA_BP_R_ROOTTP
METHOD get_instance_features.
result = VALUE #( FOR root IN roots
( %tky = root-%tky
%field-TimesChildCreated = if_abap_behv=>fc-f-read_only
) ).
ENDMETHOD.
In this simple example, the field TimesChildCreated is dynamically assigned the restriction read-only.
The annotation in $metadata is <Annotation Term="SAP__common.FieldControl" Path="__FieldControl/TimesChildCreated"/>.
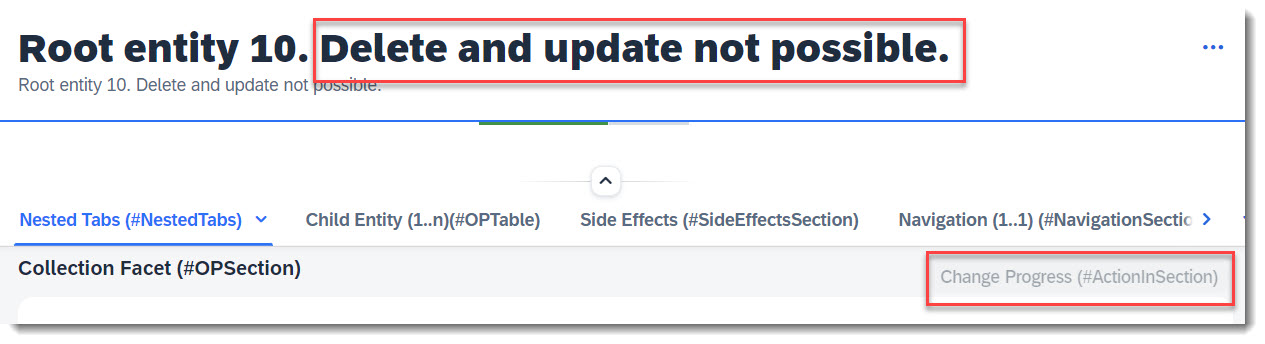
For dynamic control of operations and actions, the option (features: instance) must be added to the operation or action.
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
delete (features : instance);
action ( features : instance ) changeProgress parameter /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeProgressP result [1] $self;
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Implementation /DMO/FSA_BP_R_ROOTTP
METHOD get_instance_features.
READ ENTITIES OF /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP IN LOCAL MODE
ENTITY Root
FIELDS ( UpdateHidden DeleteHidden ) WITH CORRESPONDING #( keys )
RESULT DATA(roots)
FAILED failed.
result = VALUE #( FOR root IN roots
( %tky = root-%tky
%delete = COND #( WHEN root-DeleteHidden = abap_true
THEN if_abap_behv=>fc-o-disabled
ELSE if_abap_behv=>fc-o-enabled )
%action-changeProgress = COND #( WHEN root-UpdateHidden = abap_true
THEN if_abap_behv=>fc-o-disabled
ELSE if_abap_behv=>fc-o-enabled )
) ).
ENDMETHOD.
The delete operation and action ChangeProgress will be disabled if the fields DeleteHidden or UpdateHidden has boolean value abap_true, and vice-versa.
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Dynamic Feature Control
An action that is defined via Datafield ForAction is not tied to a specific data value. Therefore it is possible to assign the annotation to any arbitary element. Whether the action button is to be in the list report or object page, line item or section, this largely depends on the respective UI annotation you use. More examples are listed below in this guide, if you search for action.
The keyword to use for this is type: #FOR_ACTION in @UI.lineItem, @UI.fieldGroup, etc.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #OPForm
{
purpose : #HEADER, // or #STANDARD,
label : 'FieldGroup (#OPForm)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'OPForm',
id: 'SubSectionID'
}
]
@UI: {
lineItem: [
// Search Term #ActionInLineItem
{
type:#FOR_ACTION,
label: 'Change Criticality (#ActionInLineItem)',
dataAction: 'changeCriticality',
position: 10
}
],
fieldGroup: [
// Search Term #ActionInSection
{
qualifier: 'OPForm',
dataAction: 'changeProgress',
type: #FOR_ACTION,
emphasized: true,
label: 'Change Progress (#ActionInSection)'
}
]
}
LastChangedAt;
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
action changeCriticality parameter /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeCriticalityP result [1] $self;
action changeProgress parameter /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeProgressP result [1] $self;
More Information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Actions
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
An action that is tied to a data value, which would be rendered as a hyperlink. Therefore it is crucial to specify the annotation at the desired element which has the data value. Whether the action button is to be in the list report or object page, line item or section, this largely depends on the respective UI annotation you use.
The keyword to use for this is type: #WITH_ACTION in @UI.lineItem, @UI.fieldGroup, @UI.identification.
More Information:
- List Report - Content Area - Datafield WithAction in Line Item
- Object Page - Header Area - Datafield WithAction in Object Page
Search term: #ValueHelpParameter
Often properties of an entity have value helps, so that creating a new entity is easier and wrong inputs are reduced. Value helps for action parameters are also possible.
Note
Source: CDS Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeCriticalityP
// Search Term #ValueHelpParameter
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [{ entity: { name: '/DMO/FSA_I_Criticality', element: 'Code' }}]
criticality_code : abap.int4;
This can be achieved, by just annotating the parameter with @Consumption.valueHelpDefinition.
Search term: #ParameterDefaultValue
With the annotation @UI.defaultValue a default value for the parameter is set. A fixed string value can be given or a property from the entity can be reference using syntax #( 'ELEMENT_OF_REFERENCED_ENTITY: <field_name>' ).
Note
Source: CDS Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeCriticalityP
// Search Term #ParameterDefaultValue
@UI.defaultValue : #( 'ELEMENT_OF_REFERENCED_ENTITY: CriticalityCode')
criticality_code : abap.int4;
Warning
Only shown in the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
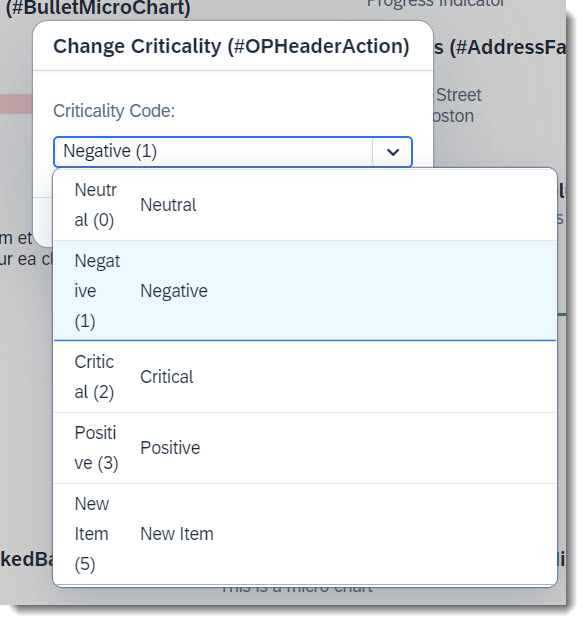
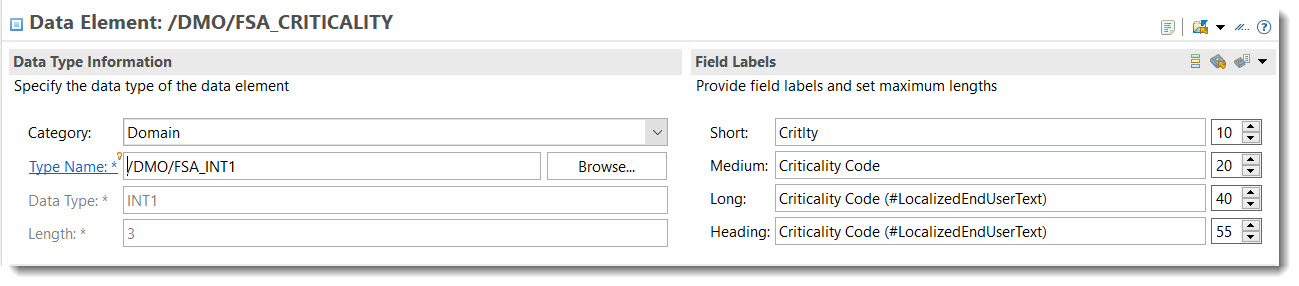
An action parameter now inherits the text label from the underlying data element. No additional effort is required other than maintaining the label (and localized text label) at the data element itself. For comparison, see the examples below.
Label from data element:
Note
Source: Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeCriticalityP
criticality_code : /dmo/fsa_criticality;
Label from annotation:
Note
Source: Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeProgressP
@EndUserText.label: 'Change Progress'
progress : abap.int4;
Search term: #IANATimezoneAParameter
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
With the annotation @Semantics.timeZone you can convert a timezone to one specified according to the IANA standard. You are also able to assign this converted timezone to a timestamp (which has to be in the UTC format) so that the time will be interpreted in this timezone. The annotation to use is @Semantics.timeZoneReference.
The conversion of the timezone is happening at the backend, while the timestamp conversion is done by the UI.
This feature is also available for general use.
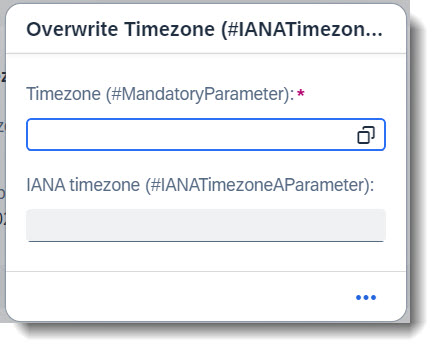
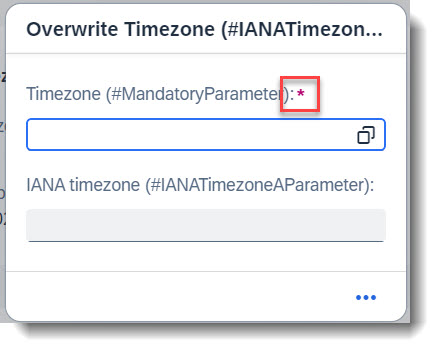
In the following example, the action overwriteTimezone expects a timezone input. Choosing a value using the value help will fill in the IANA Timezone as well.
Note
Source: Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP
@EndUserText.label: 'Oerwrite Timezone parameter'
define root abstract entity /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP
{
// Search Term #MandatoryParameter
@EndUserText.label: 'Timezone (#MandatoryParameter)'
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [{ entity: { name: 'I_TimeZoneIANACodeMap', element: 'TimeZoneID' },
additionalBinding: [{ usage: #RESULT, localElement: 'iana_timezone', element: 'TimeZoneIANACode' }] }]
sap_timezone : tznzone;
// Search Term #IANATimezoneAParameter
@Semantics.timeZone: true
@EndUserText.label: 'IANA timezone (#IANATimezoneAParameter)'
iana_timezone : tznzone;
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
...
action ( features : instance ) overwriteTimezone deep parameter /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP;
...
}
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
// Search Term #IANATimezone
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [{ entity: { name: 'I_TimeZone', element: 'TimeZoneID' } }]
SAPTimezone,
Note
Source: Metadata Extention /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
// Search Term #IANATimezone
@UI.facet: [
{
parentId : 'Nested',
id : 'TimeAndDate',
label : 'Time and Date (#TimeAndDate)',
type : #COLLECTION
},
// Search Term #IANATimezone
{
parentId : 'TimeAndDate',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'TimezoneInput',
label : 'SAP Timezone'
}
]
@UI.fieldGroup: [
{
qualifier: 'TimezoneInput',
dataAction: 'overwriteTimezone',
type: #FOR_ACTION,
emphasized: true,
label: 'Overwrite Timezone (#IANATimezoneAParameter)'
}
]
SAPTimezone;
Search term: #MandatoryParameter
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
It is possible to define mandatory parameters for action/functions but to do this, you would need a behaviour definition for the abstract entity. This is typically a deep parameter with a hierarchy structure but instead of a true hierarchy with associations, we define the abstract entity as a flat structure.
In this example, the field sap_timezone should be a mandatory parameter and will be marked with a red asterisk (*) . The keyword to use is mandatory:execute, to be marked at the field in the behaviour definition.
Note
Source: Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP
@EndUserText.label: 'Oerwrite Timezone parameter'
define root abstract entity /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP
{
// Search Term #MandatoryParameter
@EndUserText.label: 'Timezone (#MandatoryParameter)'
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [{ entity: { name: 'I_TimeZoneIANACodeMap', element: 'TimeZoneID' },
additionalBinding: [{ usage: #RESULT, localElement: 'iana_timezone', element: 'TimeZoneIANACode' }] }]
sap_timezone : tznzone;
// Search Term #IANATimezoneAParameter
@Semantics.timeZone: true
@EndUserText.label: 'IANA timezone (#IANATimezoneAParameter)'
iana_timezone : tznzone;
}
Important keywords for the behaviour definition are abstract, with hierarchy; and with control.
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP
abstract;
strict ( 2 );
with hierarchy;
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP with control
{
field (mandatory:execute) sap_timezone;
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
...
action ( features : instance ) overwriteTimezone deep parameter /DMO/FSA_D_OverwriteTimezoneP;
...
}
More information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Modeling Parameters for Non-Standard Operations
Search term: #DefaultFunctionForCreate, #DefaultFunctionForAction, #DefaultFunctionForCBA
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release.
With a default values function you can default the input parameters for actions, functions, as well as create and create-by-association operations, similar to the annotation @UI.defaultValue (see Default Value for action parameter). The difference here is, with default values function you can specify the values using more complicated coding.
The general rules are:
- Function name must begin with
GetDefaultsFor - Function name must be unique within the current BDEF
- In certain cases, external names can be given
- Key word is
{default function GetDefaultsForxxx;}behind the respective operation
The importing parameter and the return type of the function need not be specified, as they will be derived by the framework from the respective actions/operations. If you have a projection layer, it is necessary to expose the default values function too in the projection BDEF.
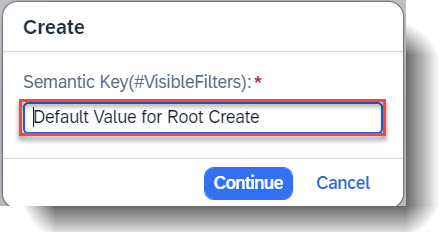
In this example, the property StringProperty, which is a mandatory input for create, will be prefilled with the value Default Value for Root Create.
Further rules:
- Function name after the keyword
default functionis optional. When specified it must beGetDefaultsForCreate - External name is not possible
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
// Search Term #DefaultFunctionForCreate
create { default function GetDefaultsForCreate; }
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP alias Root
...
{
use create;
use function GetDefaultsForCreate;
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Implementation /DMO/FSA_BP_R_RootTP
METHODS GetDefaultsForCreate FOR READ
IMPORTING keys FOR FUNCTION Root~GetDefaultsForCreate RESULT result.
METHOD GetDefaultsForCreate.
result = VALUE #( FOR key IN keys
( %cid = key-%cid
%param = VALUE #( StringProperty = 'Default Value for Root Create' ) ) ).
ENDMETHOD.
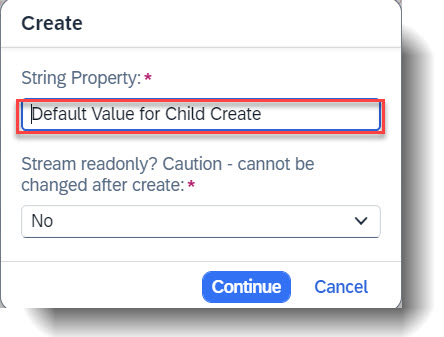
In this example, the property StringProperty, which is a mandatory input for Child create, will be prefilled with the value Default Value for Child Create. Property FieldWithPercent will also be prefilled to avoid triggering a validation error when saving (this is not shown in the pop up during create, but the code can be found in the behaviour implementation).
Further rules:
default functionmust be specified in combination with create within curly brackets for an association.- External name is possible
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
// Search Term #DefaultFunctionForCBA
association _Child { create { default function GetDefaultsForChild external 'GetDefaultsForCreateByAssociation'; } with draft; }
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP alias Root
...
{
use association _Child { create; with draft; }
use function GetDefaultsForChild;
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Implementation /DMO/FSA_BP_R_RootTP
METHODS GetDefaultsForChild FOR READ
IMPORTING keys FOR FUNCTION Root~GetDefaultsForChild RESULT result.
METHOD GetDefaultsForCreate.
result = VALUE #( FOR key IN keys
( %tky = key-%tky
%param = VALUE #( StringProperty = 'Default Value for Child Create'
FieldWithPercent = '1.0' ) ) ).
ENDMETHOD.
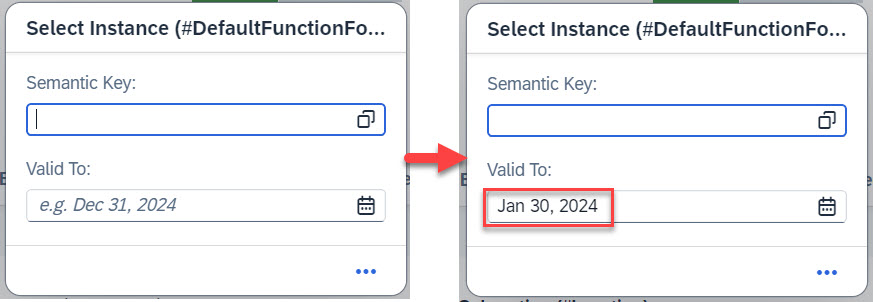
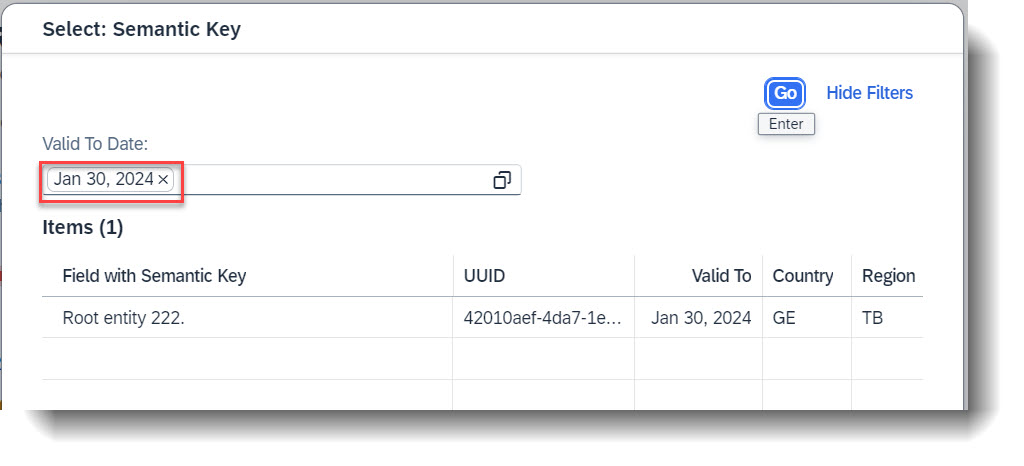
In this example, the property valid_to in input parameter /DMO/FSA_D_SelectInstanceP will be prefilled with a date. This date will in turn be used as a filter for the value help of Semantic Key.
Further rules:
- The action/function must specify an input parameter. Flat, deep, and deep table parameters are supported.
- External name is possible
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP alias Root
...
{
// Search Term #DefaultFunctionForAction
action ( features : instance ) selectInstance parameter /DMO/FSA_D_SelectInstanceP { default function GetDefaultsForSelectInstance; }
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Definition /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
define behavior for /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP alias Root
...
{
use action selectInstance;
use function GetDefaultsForSelectInstance;
}
Note
Source: Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_SelectInstanceP
// Search Term #DefaultFunctionForAction
define abstract entity /DMO/FSA_D_SelectInstanceP
{
@Consumption.valueHelpDefinition: [{ entity: { name: '/DMO/FSA_RootVH' , element: 'StringProperty' },
additionalBinding: [{ element: 'ValidTo',
localElement: 'valid_to',
usage: #FILTER }] }]
@EndUserText.label: 'Semantic Key'
string_property : abap.char(256) ;
@EndUserText.label: 'Valid To'
valid_to: abap.dats;
}
Note
Source: Behaviour Implementation /DMO/FSA_BP_R_RootTP
METHODS GetDefaultsForSelectInstance FOR READ
IMPORTING keys FOR FUNCTION Root~GetDefaultsForSelectInstance RESULT result.
METHOD GetDefaultsForSelectInstance.
DATA: lv_validto TYPE d.
SELECT SINGLE validto
FROM /DMO/FSA_RootVH
WHERE validto IS NOT INITIAL
INTO @DATA(lv_validto).
result = VALUE #( FOR key IN keys
( %tky = key-%tky
%param = VALUE #( valid_to = lv_validto ) ) ).
ENDMETHOD.
More information: ABAP RESTful Application Programming Model - Operation Defaulting
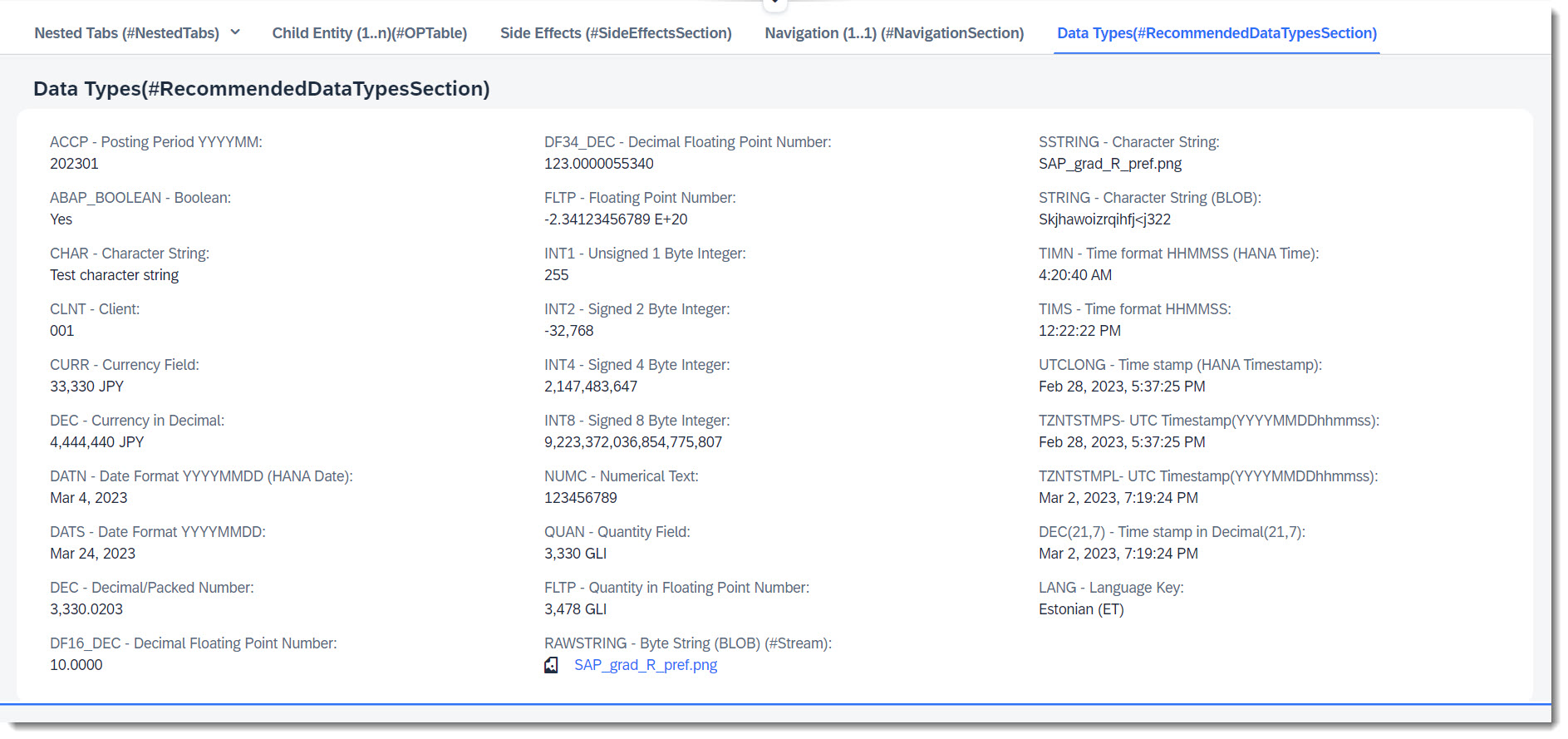
Search term: #RecommendedDataTypesSection
To define the data model of our business object, we have to create tables to store the data that the CDS view is built upon. For the backend to derive the correct data types for oData, there is a list of recommended, released built in ABAP types and data elements that you can use. There are used in the app and can be seen in the Object Page under Data Types(#RecommendedDataTypesSection).
Note
Source: Database Table /DMO/FSA_Root_A
define table /dmo/fsa_root_a {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
...
type_accp : abap.accp;
type_bool : abap_boolean;
type_char : abap.char(256);
type_clnt : abap.clnt;
type_cuky : abap.cuky;
@Semantics.amount.currencyCode : '/dmo/fsa_root_a.type_cuky'
type_curr : abap.curr(10,2);
type_dec_amount : abap.dec(10,2);
type_datn : abap.datn;
type_dats : abap.dats;
type_dec : abap.dec(12,4);
@AbapCatalog.decfloat.outputStyle : #NORMAL
type_df16_dec : abap.df16_dec(10,4);
type_fltp : abap.fltp;
type_int1 : abap.int1;
type_int2 : abap.int2;
type_int4 : abap.int4;
type_int8 : abap.int8;
type_lang : abap.lang;
type_numc : abap.numc(128);
@Semantics.quantity.unitOfMeasure : '/dmo/fsa_root_a.type_unit'
type_quan : abap.quan(20,4);
type_fltp_quan : abap.fltp;
type_rawstring : abap.rawstring(0);
type_sstring : abap.sstring(256);
type_string : abap.string(0);
type_timn : abap.timn;
type_tims : abap.tims;
type_unit : abap.unit(3);
type_tzntstmps : tzntstmps;
type_tzntstmpl : tzntstmpl;
type_dec_time : abap.dec(21,7);
type_utclong : abap.utclong;
stream_mimetype : abap.char(128);
@AbapCatalog.decfloat.outputStyle : #NORMAL
type_df34_dec : abap.df34_dec(31,10);
}
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
annotate entity /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP with
{
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #RecommendedDataTypesSection
{
purpose: #STANDARD,
type: #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'DataTypes',
label: 'Data Types(#RecommendedDataTypesSection)'
}
]
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 10, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeAccp;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 20, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeBool;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 30, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeChar;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 40, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeClnt;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 50, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeCurr;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 60, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeDecAmount;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 70, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeDatn;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 80, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeDats;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 90, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeDec;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 100, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeDf16Dec;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 110, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeDf34Dec;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 120, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeFltp;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 130, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeInt1;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 140, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeInt2;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 150, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeInt4;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 160, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeInt8;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 170, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeNumc;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 180, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeQuan;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 190, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeFltpQuan;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 200, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeRawstring;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 210, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeSstring;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 220, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeString;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 230, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeTimn;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 240, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeTims;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 250, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeUtclong;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 260, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeTzntstmps;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 270, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeTzntstmpl;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 280, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeDecTime;
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ position: 290, qualifier: 'DataTypes' }]
TypeLang;
}
Search term: #QuickView
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
A quick view is a pop up that shows more information, when you click on an entry in a column or an object page. Typically, it is used in combination with one-to-one or zero-to-one associations. By clicking on the link, more information about the associated entity can be displayed.
To enable a quick view facet, the association entity needs to be annotated with @UI.facet with type: #QUICK_VIEW. For a better looking header of the quick view, the association entity gets typically annotated with @UI.headerInfo. Additionally, the key value can be replaced with another text property using @ObjectModel.text.element, so that the column is readable.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Navigation
@UI.headerInfo: {
typeName: 'Navigation',
typeNamePlural: 'Navigations',
title.value: 'StringProperty',
description.value: 'StringProperty',
typeImageUrl: 'sap-icon://blank-tag'
}
// Search Term #QuickView
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Navigation
...
{
@UI.facet: [
{
type: #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
label: 'Navigation',
targetQualifier: 'data',
purpose: #QUICK_VIEW
}
]
@ObjectModel.text.element: ['StringProperty'] // Search Term #DisplayTextAndID
key id as ID,
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ qualifier: 'data', position: 10 }]
string_property as StringProperty,
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ qualifier: 'data', position: 20 }]
integer_property as IntegerProperty,
@UI.fieldGroup: [{ qualifier: 'data', position: 30 }]
decimal_property as DecimalProperty,
...
}
Search term: #QuickViewNullValueIndicator
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
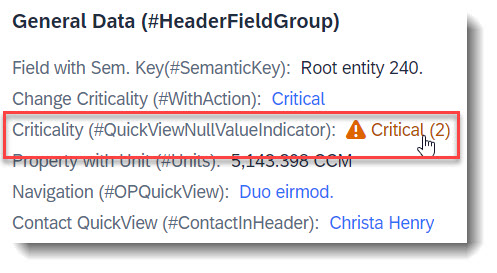
When your associated entity (QuickView entity) has a key that is non-UUID, a referential constraint for the association does not get generated automatically. To do so, a property needs to act as a null value indicator for the QuickView property, similar to a value control property, using the annotation @Semantics.nullValueIndicatorFor.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Root
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Root
...
association [0..1] to /DMO/FSA_I_Criticality as _Criticality on $projection.CriticalityCode = _Criticality.Code
{
@ObjectModel.foreignKey.association: '_Criticality'
criticality_code as CriticalityCode, // Property for QuickView link
// Search Term #QuickViewNullValueIndicator
@Semantics.nullValueIndicatorFor: 'CriticalityCode'
cast(' ' as abap_boolean preserving type ) as CriticalityNullValInd, // Null value indicator
...
}
Then setup your QuickView entity as usual.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Criticality
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Criticality
...
{
// Search Term #QuickViewNullValueIndicator
@UI.facet: [
{
type: #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
label: 'Criticality QuickView(#QuickViewNullValueIndicator)',
targetQualifier: 'QuickView',
purpose: #QUICK_VIEW
}
]
@UI: {
fieldGroup: [
{
qualifier: 'QuickView',
position: 10
}
]
}
key code as Code,
// Search Term #QuickViewNullValueIndicator
@UI.fieldGroup: [
{
qualifier: 'QuickView',
position: 20
}
]
descr as Description
}
And finally add your QuickView property to your app, in this example, using fieldgroup.
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
@UI.facet: [
// Search Term #HeaderCollectionFacet
{
purpose: #HEADER,
id: 'FacetCollection',
type: #COLLECTION
},
// Search Term #HeaderFieldGroup
{
parentId : 'FacetCollection',
label : 'General Data (#HeaderFieldGroup)',
type : #FIELDGROUP_REFERENCE,
targetQualifier: 'HeaderData'
}
]
@UI: {
fieldGroup: [
// Search Term #QuickViewNullValueIndicator
{
qualifier: 'HeaderData',
criticality: 'CriticalityCode',
position: 50,
label: 'Criticality QuickView(#QuickViewNullValueIndicator)'
}
]
}
CriticalityCode; // Property for QuickView link
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2022 onwards.
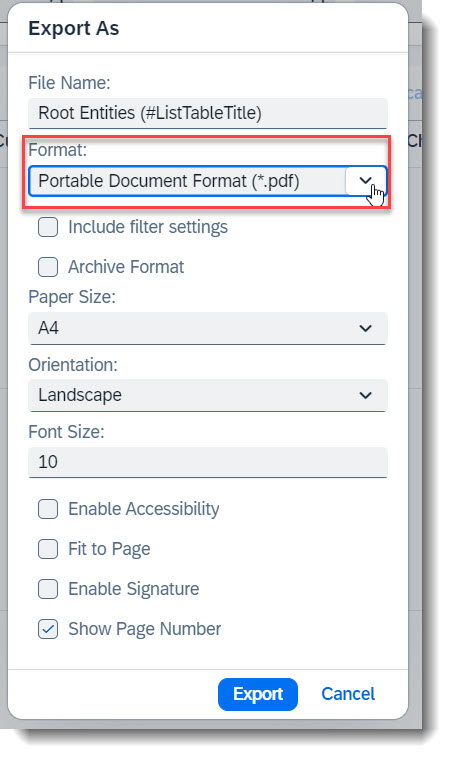
It is possible to download a copy of the records in List Report in the format PDF/A without any additional configuration. Take note that not all data types are supported, i.e. Stream properties are ignored.
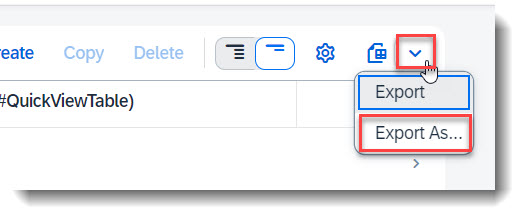
To control which columns are to be exported, first adjust your List Report View Settings and select the columns to be shown. Then click the Dropdown button, which is next to the Export File button and choose Export As..., or use the shortcut key Ctrl+Shift+E. Select the format Portable Document Format (*.pdf) in the popup box and additional settings will appear. Click the Export button to start your download.
The file will be exported to your Downloads folder for both Windows and MacOS.
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release.
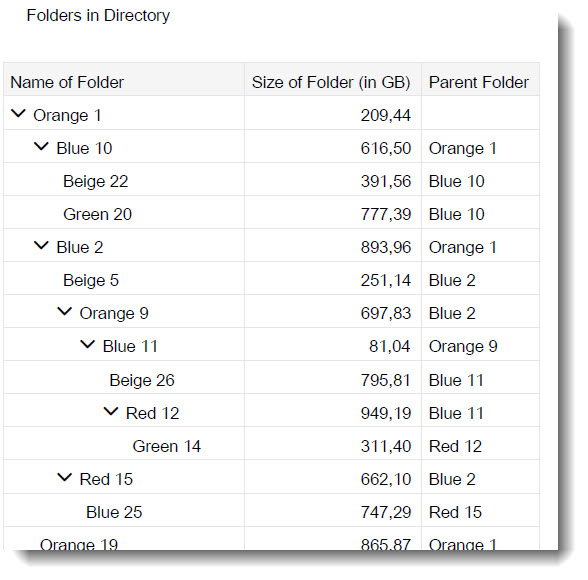
It is possible to download a treeview in the format PDF/A without any additional configuration. Take note that not all data types are supported, i.e. Stream properties are ignored.
To control which columns are to be exported, first adjust your treeview settings and select the columns to be shown. Then click the Dropdown button, which is next to the Export File button and choose Export As..., or use the shortcut key Ctrl+Shift+E. Select the format Portable Document Format (*.pdf) in the popup box and additional settings will appear. Click the Export button to start your download.
The file will be exported to your Downloads folder for both Windows and MacOS.
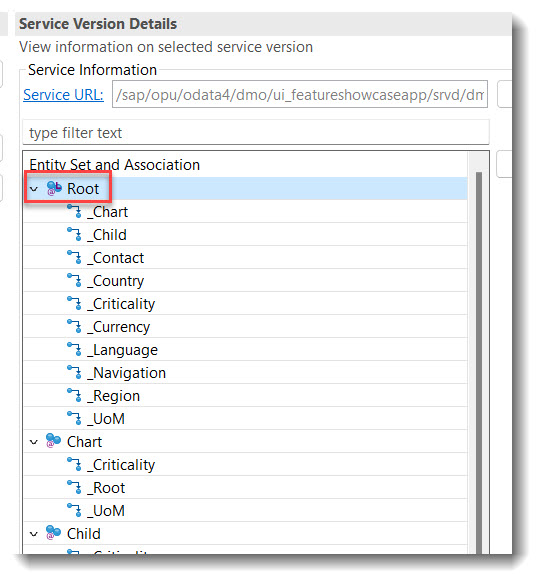
Search term: #LeadingEntity
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release and for SAP S/4HANA, on-premise edition or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, private edition, from release 2023 onwards.
In a service definition, it is possible to annotate the leading entity of a service binding using annotation @ObjectModel.leadingEntity.name. This will make it easier for a user to find the starting node to start the app preview in a service binding. The leading node will have a tiny 'L' at the entity.
Note
Source: Service Definition /DMO/UI_FeatureShowcaseApp
@ObjectModel.leadingEntity.name: '/DMO/FSA_C_RootTP'
define service /DMO/UI_FeatureShowcaseApp {
...
AdaptationHidden
Search term: UI.adaptationHidden
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release.
Important
UI Adaptation is only possible with deployed apps. Therefore some features of this annotation cannot be showcased in the Feature Showcase App app preview, unless stated otherwise.
UI adaptation is a feature of SAPUI5 flexibility that allows key users without technical knowledge to easily make UI changes for all users of an app, end users to personalize controls, and developers to extend the UIs of SAPUI5 applications. For more information, see SAPUI5 Flexibility: Adapting UIs Made Easy.
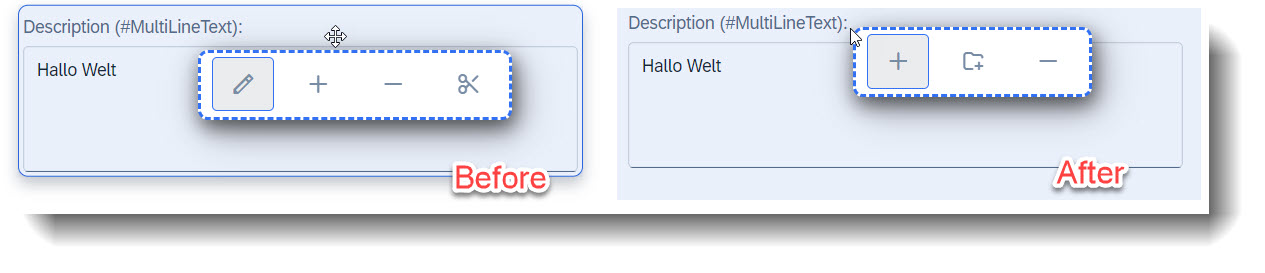
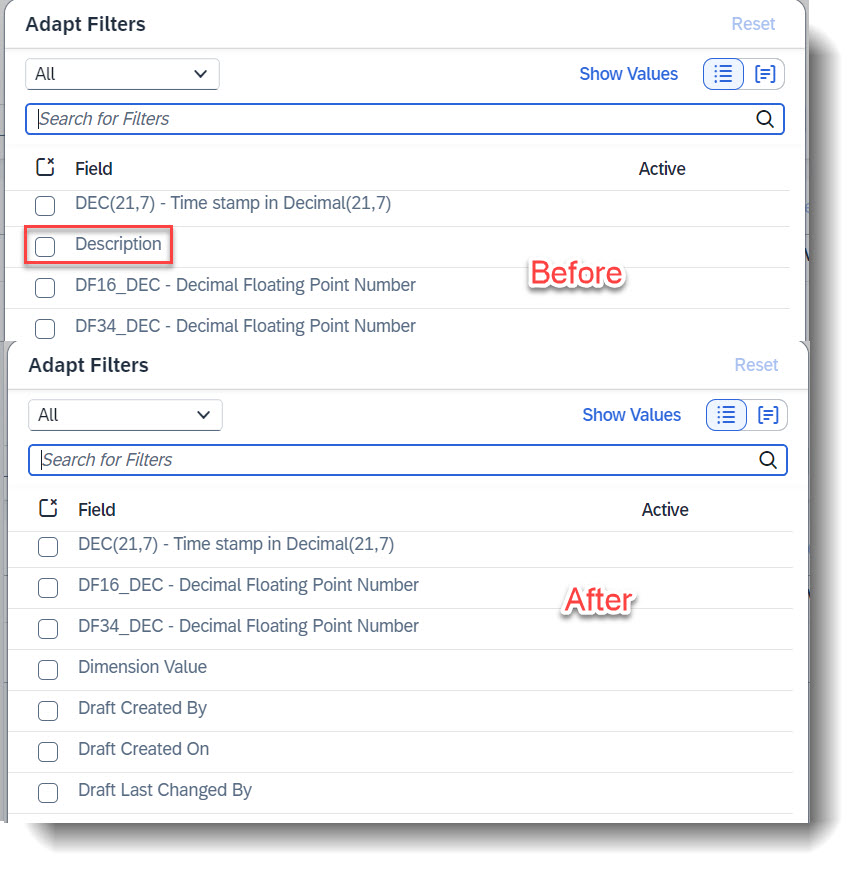
But there are some scenarios where you do not want to allow this, that a specific property or entity should only adher to the metadata or annotations. It is possible to do this, by using the annotation @UI.adaptationHidden: true.
As a result, the property Description cannot
- be removed or added in, in the object page
- have its label/description be edited
- have its position on the object page be changed via drag-and-drop
In addition to the above, the property Description cannot
- be added in as a list report filter
Note
Source: Metadata Extension /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP
annotate entity /DMO/FSA_C_RootTP with
{
@UI.adaptationHidden: true
Description;
}
More Information: SAP Fiori Launchpad - Making UI Adaptations
Search term: #SimpleType
Warning
Only available with the latest SAP BTP or SAP S/4HANA Cloud, public edition release.
Simple types allow the definition of user-defined scalar types together with (arbitrary) domain-specific metadata via CDS annotations.
Simpler put, you can create user-defined data types in ABAP CDS, which work similarly to Data Elements in DDIC. The advantages of CDS simple types are:
- you can type them to build-in data types like
abap.int4, DDIC data elements, or even other CDS simple types - you can use a fixed list of CDS annotations to enrich the metadata of these data types, including but not limited to:
EndUserText,Semantics, and others
Tip
To get the full list of allowed annotations in simple type, simply use Code Completion in ADT with Ctrl + Space after typing @
These data types can be used in CDS views by view parameters directly, or by properties via casting, and also directly by parameters in abstract entities. You can also use them in your ABAP code, especially when you are developing the behaviour implementation of RAP business objects.
Warning
Do not use CDS Simple Type with enumeration as it is not supported in RAP. CDS Simple Type is not supported in classic DDIC like tables and structures
Note
Source: Type /DMO/FSA_BT_Integer
@EndUserText.label: 'Integer Value(from Simple Type)'
@EndUserText.quickinfo: 'Integer Value'
@EndUserText.heading: 'Integer'
// Search Term #SimpleType
define type /DMO/FSA_BT_Integer: abap.int4
The simple type /DMO/FSA_BT_Integer is typed to a build-in data type and enriched with @EndUserText annotations.
Note
Source: Type /DMO/FSA_BT_ProgressInteger
@EndUserText.label: 'Progress Integer Value(from Simple Type)'
@EndUserText.quickinfo: 'Progress Integer Value'
@EndUserText.heading: 'Progress Integer'
// Search Term #SimpleType
define type /DMO/FSA_BT_ProgressInteger: /DMO/FSA_BT_Integer
Note
Source: Type /DMO/FSA_BT_RadialInteger
@EndUserText.label: 'Radial Integer Value(from Simple Type)'
@EndUserText.quickinfo: 'Radial Integer Value'
@EndUserText.heading: 'Radial Integer'
// Search Term #SimpleType
define type /DMO/FSA_BT_RadialInteger: /DMO/FSA_BT_Integer
The simple types /DMO/FSA_BT_ProgressInteger and /DMO/FSA_BT_RadialInteger are typed to another simple type, otherwise known as stacking. The types will also inherit the annotations of the base type, or they can be overwritten, as is the case here.
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_I_Root
define view entity /DMO/FSA_I_Root...
{
...
cast ( integer_value as /DMO/FSA_BT_Integer preserving type ) as IntegerValue, // Search Term #SimpleType
}
Note
Source: CDS View /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP
define root view entity /DMO/FSA_R_RootTP...
{
...
cast ( IntegerValue as /DMO/FSA_BT_RadialInteger preserving type ) as RadialIntegerValue, // Search Term #SimpleType
cast ( IntegerValue as /DMO/FSA_BT_ProgressInteger preserving type ) as ProgressIntegerValue, // Search Term #SimpleType
}
Note
Source: Abstract Entity /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeProgressP
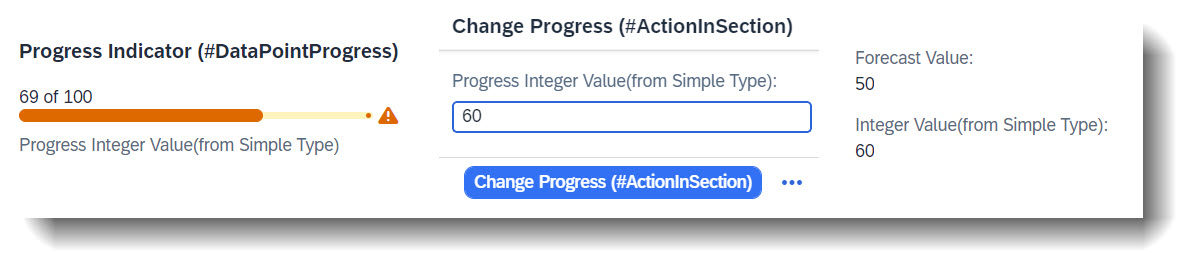
define abstract entity /DMO/FSA_D_ChangeProgressP
{
progress : /DMO/FSA_BT_ProgressInteger; // Search Term #SimpleType
}
All types are now used in CDS views and abstract entity and will inherit the text annotations from the simple type definition, which will be shown in UI.
More Information:
- ABAP Data Models - Simple Types
- ABAP CDS Releases CDS-Native Data Types: CDS Simple Types
- ABAP Cloud: CDS Simple Types